MySQL学习笔记4
其他查表操作
NULL
Conceptually, NULL means “a missing unknown value” and it is treated somewhat differently from other values.
To test for NULL, use the IS NULL and IS NOT NULL operators, as shown here:
SELECT 1 IS NULL, 1 IS NOT NULL; |
You cannot use arithmetic comparison operators such as =, <, or <> to test for NULL.
计算满足条件的行数
使用COUNT(*)计算行数,结合GROUP BY可以实现更多自定义筛选,比如:
对于表student:
+--------+------+------------+ |
可以计算不同性别以及未填写性别信息的学生数量:
SELECT sex, COUNT(*) AS count FROM student GROUP BY sex; |
(In this output, NULL indicates that the sex is unknown.)
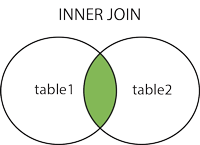
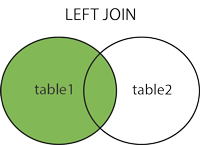
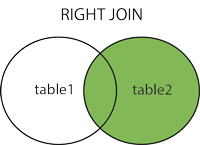
JOIN
JOIN是将多张表进行合并的方法,主要有 Inner join和 Outer join,详情见维基百科这里。
另外,还有一种Self-join比较特殊,是一张表的2份拷贝做 Inner join。
Inner join会对两张表做笛卡尔积。
Outer join包括LEFT JOIN和RIGHT JOIN,以上3种JOIN的解释可见这里,有图如下:
常见查表范例
查找极值
使用MAX()和MIN(),比如对于上面的表student,可以取日期的最大值,最小值和各自的完整行信息如下:
SELECT MAX(birth) FROM student ; |